Atlanta's Trusted Orchiectomy Specialists
What is an Orchiectomy?
An orchiectomy is a surgical procedure to remove one or both testicles, the organs responsible for producing sperm and the male hormone testosterone. Testicles are located in the scrotum, a sac of skin beneath the penis. This procedure is commonly used to treat or prevent testicular cancer, prostate cancer, and male breast cancer.
It is also a key part of the gender transition process for transgender women. Orchiectomy is typically an outpatient surgery, allowing patients to return home the same day.
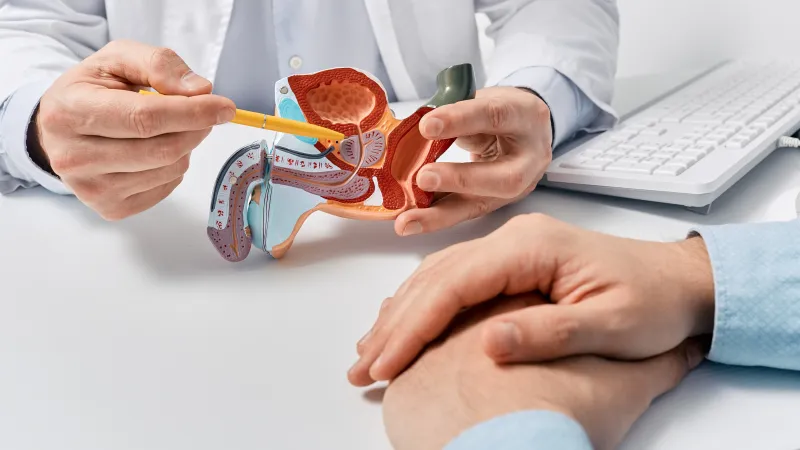
Benefits of Orchiectomy
Orchiectomy offers several benefits depending on the reason for the surgery:
- Effective Cancer Treatment: For testicular, prostate, and male breast cancers, orchiectomy effectively reduces male hormone levels and helps shrink cancerous tumors. It also provides a tissue sample for accurate diagnosis.
- Gender Affirmation: For transgender women, orchiectomy is a key component of gender transition, reducing the need for long-term hormone therapy. This can help minimize the risks associated with estrogen supplements, such as blood clots.
- Trauma Repair: For individuals with severely damaged testicles, orchiectomy prevents complications and relieves pain.

Potential Side Effects and Risks
While orchiectomy is safe, the sudden drop in hormone levels can cause side effects such as:
- Hot flashes
- Reduced libido
- Fatigue
- Emotional changes