Overactive Bladder Treatment in Atlanta
What is Overactive Bladder?
Overactive bladder (OAB) causes sudden, strong urges to urinate, frequent urination, and possible urine leakage (urgency incontinence), often leading to self-consciousness and avoiding social activities, but effective treatments are available.
We Offer The Best Treatment For Overactive Bladders In Atlanta
At Advanced Urology, we proudly offer the best treatment for overactive bladders in Atlanta, boasting up to an 85% success rate. Our expert doctors are dedicated to helping you regain control and improve your quality of life.
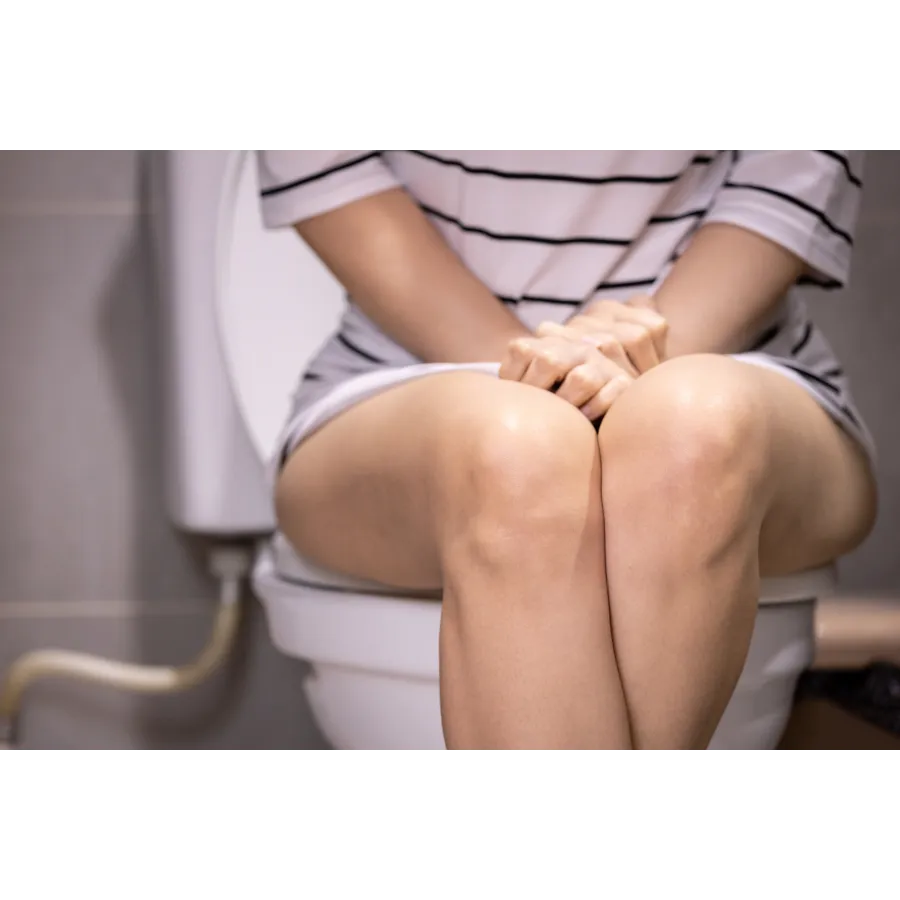
Common Signs & Symptoms Of An Overactive Bladder
- Urgency to urinate
- Frequent urination
- Nocturia
- Urge incontinence
- Inability to hold urine
- Small urine output
- Interruption of daily activities
- Bladder discomfort
- Urgency triggered by sounds or sights
- Anxiety about proximity to bathroom
Possible Causes
Of An Overactive Bladder
There are several potential causes of an overactive bladder, including nerve damage from conditions like stroke or multiple sclerosis, and weakened pelvic muscles due to childbirth or aging. Other factors such as urinary tract infections, bladder abnormalities, excessive fluid intake, certain medications, hormonal changes, obesity, neurological disorders, and bladder muscle dysfunction can also contribute to this condition.
When to See a Doctor for an Overactive Bladder
Many people associate overactive bladder with frequent urges to urinate, but symptoms can range from minor inconvenience to significant disruption in daily life, depending on factors like severity and frequency. Many patients experience overactive bladder without ever receiving a comprehensive evaluation to identify the root cause. At Advanced Urology, we evaluate the underlying factors contributing to overactive bladder.
We can help manage overactive bladder symptoms before they worsen. If you have a history of overactive bladder, addressing the issue early can reduce the likelihood of symptoms progressing. It's important to consult a doctor if you're experiencing frequent, urgent urges to urinate, particularly if they disrupt your daily activities or cause embarrassment.
Signs such as frequent urination day and night, urine leakage, or difficulty holding urine should not be ignored. Seek medical attention if overactive bladder symptoms are significantly impacting your quality of life. Although overactive bladder is common, it is not a normal part of aging, and effective treatments are available to help manage it.
Schedule Appointment Online
Schedule Appointment Online
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Overactive Bladder
Q Who is most at risk for developing an overactive bladder?
Overactive bladder can affect anyone, but certain factors increase the risk. Older adults, especially those over 60, are more likely to experience OAB due to age-related changes in the bladder. Women may be at higher risk due to hormonal changes after menopause or pelvic floor issues from childbirth. Other risk factors include obesity, neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis, and a history of bladder infections or surgeries.
Q How do people manage an overactive bladder?
Lifestyle changes can significantly help manage overactive bladder. Reducing the consumption of bladder irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods can minimize symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking can also improve bladder health. Bladder training, which involves gradually increasing the time between urination and pelvic floor exercises, like Kegels, can strengthen bladder control. Drinking fluids in moderation and at appropriate times, such as limiting intake before bedtime, can also reduce the frequency of urination.
Q How is overactive bladder diagnosed?
Overactive bladder is diagnosed through a combination of methods. A healthcare provider will typically review your medical history, perform a physical examination, and conduct a urinalysis to check for infections or blood in the urine. Other diagnostic tools may include keeping a bladder diary to track urination patterns, measuring postvoid residual urine to determine how much urine remains in the bladder after urination, and performing urodynamic tests to assess bladder function.
Q What treatment options are available for overactive bladder?
Overactive bladder treatments vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. Common treatments include lifestyle modifications such as bladder training and dietary changes, pelvic floor exercises to strengthen the muscles that control urination, medications to relax the bladder, and, in some cases, minimally invasive procedures like Botox injections or nerve stimulation therapies. For severe cases, surgical interventions may be recommended. Consulting with a specialist can help determine the best treatment plan.