January 20, 2020
By Dr. Vahan Kassabian and Dr. A. Dev Mally, Advanced Urology
Updated 9:26 AM ET, Mon Jan 20, 2020
Atlanta Prostate Center: Prostate Cancer Overview
Prostate cancer is common among men over the age of 65. It rarely affects men below the age of 40. Prostate cancer is the most common solid organ cancer diagnosed in American men, and the second leading cause of cancer death in American Men. Every 18 minutes, one American man dies of prostate cancer. According to a report by the National Cancer Institute:
- Prostate cancer accounts for 9.5 percent of all new cancer cases in the US.
- 164,690 prostate cancer cases have been reported in 2018.
- Prostate cancer accounts for almost 30,000 deaths annually.
- 11.2 percent of men are likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer.
- More than three million American men have been diagnosed with prostate cancer.
Understanding the Prostate
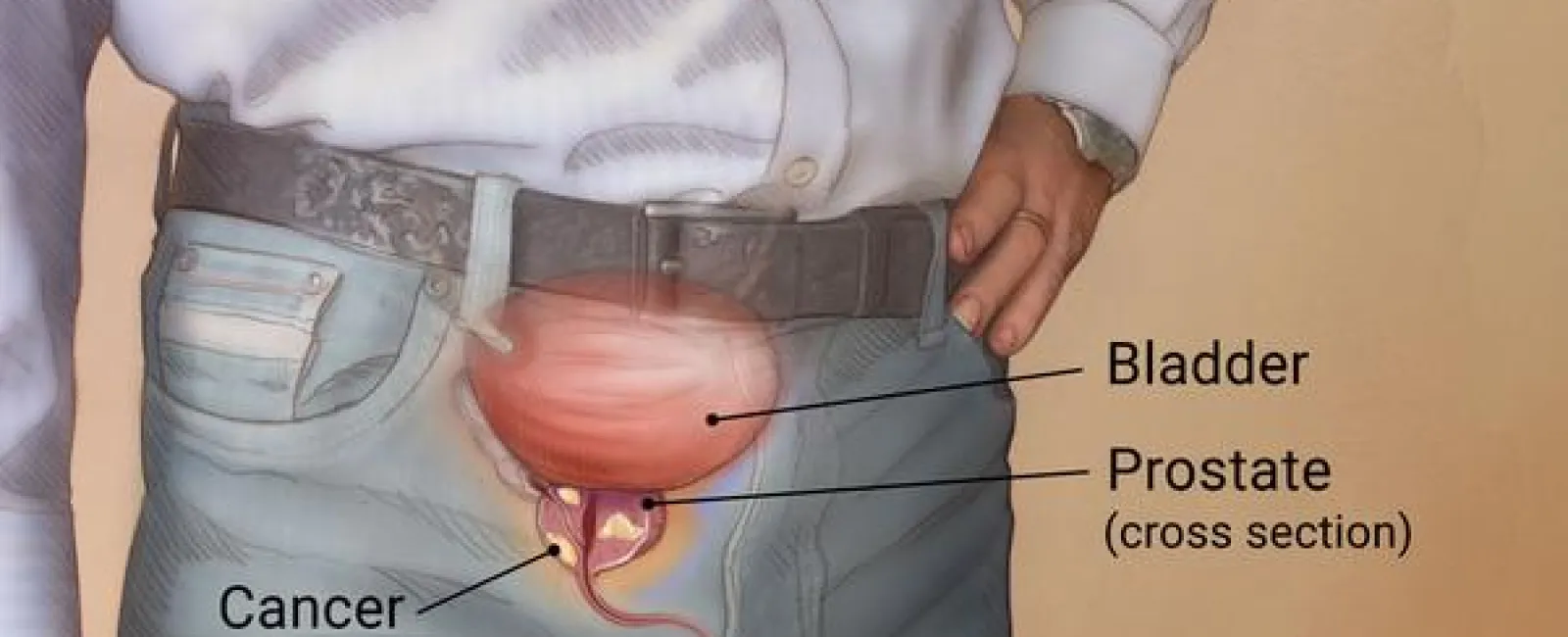
- The prostate is an integral gland of the male reproductive system. Cancer of the prostate occurs when cells in the prostate gland start to multiply at an uncontrollable rate. This is mainly caused by the mutation of cells. The cells are kept in check by the body's immune system. However, if the mutated cells multiply, they grow into a tumor, and this causes cancer.
- The prostate is a gland located just below the bladder. It plays a dual role of producing the fluid found in semen (seminal fluid) and controls urine. The seminal fluid protects sperm as they travel toward an egg. The prostate gland is active during ejaculation. During this period, sperms are ejected from the testes to the prostate. The seminal fluid is propelled into the urethra by the muscles of the prostate gland.
Causes of Prostate Cancer
While the precise causes of prostate cancer are still unknown, doctors and scientists have identified several risk factors. It has been highlighted earlier on that prostate cancer is caused by the mutation of DNA in the prostate cell. DNA is the basic component of the cells that make up genes.
Genes are responsible for the function of the cells. They also control how the cells divide, grow, and die. This is the cell life cycle.
There are two types of genes:
- Oncogenes - They are responsible for cell growth and division. They also keep the cells alive.
- Tumor suppressor genes - They control cell growth, repair in faults found in the DNA, and see to it that cells die when they are supposed to.
About Prostate Cancer
- Compared to other cancers, prostate cancer has the third highest number of cancer-related deaths. It is also the highest non-skin cancer that affects Americans.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
DNA mutations can result in cancer. The changes in DNA can come from a person's parents or they can develop them along the way.
Inherited Gene Mutation (GENETIC)
Inherited gene mutations account for about five to ten percent of all reported prostate cancer cases. This is known as hereditary prostate cancer. Common genes include BRCA1, BRCA2 and HOXB13.
Acquired Gene Mutation (SOMATIC)
The DNA changes are only found in the cell that caused the mutation. Being exposed to cancer-causing chemicals can trigger the mutation.
Age
Prostate cancer frequently affects older men. Young men are at a lower risk while men age 60 and over have a higher risk of being diagnosed with cancer.
Race
Although there is no scientific explanation for this, African-American men are at higher risk of developing prostate cancer as compared to Asian-American and Latino men. Moreover, African-American are more likely to die from prostate cancer than white men. In areas with higher concentrations of older African American men such as cities like Atlanta, Georgia, prostate cancer rates are higher than average. It appears that African American men respond better to immunotherapy than Caucasian men.
Diet
Eating a lot of red meat and high diary-fat products increases the chances of developing prostate cancer, although the research in this area is not yet completely conclusive.
Location
Men living in North America, Australia, and the Caribbean are more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer than men living anywhere else.
Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Most prostate cancer has no symptoms, especially in the early stages. It is difficult to see or discover unless a person visits the doctor to get a medical checkup. Annual check ups including a DRE (Digital Rectal Exam) and a PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen) blood test are the best way to catch the disease early.
Some of the common prostate cancer symptoms to look out for include:
- Inability to urinate
- Difficulties in controlling the beginning and end of urine flow
- Passing urine frequently mostly during the night
- Feeling pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Erectile problems
- Presence of blood in the urine or semen
- Frequent pain in the lower back, pelvis, hip or belly
Because the prostate cancer survival rate is much higher in the early stages, it's critical that you keep a watch over your prostate health as you age. It is important to note that these symptoms may also be caused by benign conditions of the prostate. Only your doctor can differentiate cancer from benign conditions.
Healthy Lifestyle Tips for Prostate Cancer
Healthy Diet
A diet consisting of fruit and vegetable contains vital nutrients that contribute to an overall good health. Men are urged to avoid foods high in fat.
Exercise
Exercising is a good way of improving a person's health. It helps to maintain a good weight. Men who don't exercise have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
Regular Screenings
A regular doctor's visits help to detect prostate cancer in its early stage. Just like any other cancer, early detection is an important factor in the success of cancer treatment.
The following factors can cause aggressive cancer that may be difficult to treat:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Consuming a high amount of calcium
The following factors do not seem to have a risk:
- Sexual activity
- Vasectomy
- Alcohol consumption
Prostate Cancer Stages
There are a number of stages in the development of prostate cancer. These stage help doctors to figure the best possible treatment plan to use.
These stages determine the severity and how far cancer may have spread.
Stage I
The tumor is small and invisible to the human eye. It is usually found due to an PSA (blood test). The cancer is still localized in the prostate and hasn't spread to other areas.
Stage II
The cancer is still confined to the prostate. A digital rectal exam or PSA can be used to detect the tumor.
Stage III
The cancer has spread outside of the prostate, possibly to other areas such as the seminal vesicles.
Stage IV
The cancer has spread to other areas near the prostate gland such as the bladder, rectum, lymph nodes, bone or other organs.
What to Expect When Seeking Treatment for Prostate Cancer
The treatment of prostate cancer will depend on a number of factors such as:
- The number of cells that have mutated (tumor aggressiveness)
- The spread of the tumor (prostate cancer stage)
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood test levels
- Individual health factors (age, health, etc)
The tests used to diagnose prostate cancer include:
- Digital rectal examination
- PSA
- Other methods may include
- Biomarker test which checks blood, urine, or body tissue samples
- PCA3 test/ 4K test
- Transrectal ultrasound
- T3 MRI of Prostate
- Prostate biopsy
If your cancer has not yet spread, treatment is either with surgery, radiation, cryotherapy, HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound, or active surveillance. For prostate cancer in advanced stages, immunotherapy, chemotherapy or other medications may be recommended.
If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, contact your doctor or urologist immediately. Prostate cancer can go undetected before it spreads to other organs.
It's important to be tested early.
When to See an Atlanta Doctor for Prostate Cancer
If you suspect you have prostate cancer or if you're suffering from any of the symptoms listed above, it's important to schedule an appointment with your doctor or urologist immediately. Catching the cancer early increases the chance to eliminate the cancer entirely. Chances are, you've begun researching treatment options online using searches like "prostate cancer doctor near me" or "urologist cancer treatment near me." If this is you, Advanced Urology can help. As a man gets older, his doctor will check the prostate during routine annual check-ups. Screening for prostate cancer includes 1. A rectal exam to feel the prostate as well as 2. A blood test to check the PSA (a protien made by the prostate). Get tested at an Atlanta urologist as soon as possible.
Diagnosis and Testing of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer other than skin cancer affecting men in the United States.
It isn't clear what causes prostate cancer, but we do know how it happens. Cells in your prostate mutate and aggressively multiply. This causes a tumor to form either on or inside of the prostate. Since most prostate cancer patients have no symptoms, it is important to get routine screening including a rectal exam and a blood test. If either of these are abnormal, a prostate biopsy is usually the next step to confirm if you have prostate cancer.
When You Need to Be Tested in Atlanta for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer affects millions of Americans and people worldwide. Most people with prostate cancer have no symptoms and it is caught incidentally by your primary care doctor usually either on rectal exam or on routine blood test (an elevated PSA). If either of these are abnormal, or if you have not had either of these tests done, then you should see a Urologist with Advanced Urology. Usually symptoms such as weak urine stream, waking up at night are due to an enlarged prostate and not prostate cancer, though in some advanced prostate cancers, they can present as bothersome urinary symptoms. Both of these issues are treated by urologists at Advanced Urology.
Getting Tested for Prostate Cancer in Atlanta, GA
If you suspect you have prostate cancer or if you're suffering from any of the symptoms listed above, it's important to schedule an appointment with your doctor or urologist immediately. If your doctor suspects prostate cancer, a series of test will be performed for an accurate diagnosis.
- Blood testing - An elevated PSA (checked with a simple blood test) may indicate that you have prostate cancer.
- Rectal exam - This is done by your doctor to feel the prostate and can detect some prostate cancers
- Image testing - A CT scan, bone scan or MRI is not routinely checked, though it is done in select cases to evaluate the extent of disease spread.
- Biopsy - If you have either an abnormal PSA on routine blood test or if you have an abnormal rectal exam, the next step is usually to do a prostate biopsy. This is done with the aid of an ultrasound to biopsy high risk areas of the prostate.
It's essential that you get tested as soon as possible if you suspect you may have prostate cancer.
Medications and Supplements used in Prostate Cancer Treatment
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in the United States. It's not entirely known why but many doctors believe it has to do with lifestyle and eating habits. In some cases, it's even genetic.
If you have less aggressive prostate cancer, we can place you on active surveillance, where we periodically check your PSA (blood test) and do rectal exams, and prostate biopsies. If your cancer becomes more aggressive, then treatment would be recommended. Standard of care treatment options include surgery and/or radiation. Other options include High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU), though not currently standard of care, and not recommended for high risk disease as its effectiveness is still being studied. For high risk disease, they may need both surgery and radiation. Usually chemotherapy or other medications are not needed to treat prostate cancer, unless it is in an advanced stage and has spread to other parts of the body.
Nonsurgical Treatments for Prostate Cancer in Atlanta
Surgery now can be done in most people in a minimally invasive fashion using the DaVinci robot, and most people can go home the next day after surgery. Most people can then resume normal activity in about 1 month without restrictions.
Non-surgical options for treatment of prostate cancer that has not spread, standard of care options includes surgery radiation. Radiation uses high-powered energy beams to kill the cancer. If you have had radiation to the prostate, it is very difficult to do surgery afterwards if the cancer recurs. Furthermore, risk of complications increases if surgery is done after radiation. If surgery is done before radiation, these risks are usually much lower. Most people who have surgery do not need radiation afterwards.
Cryotherapy can also be used to treat the prostate using cold probes placed in the gland through the perineum. This can also be done if the cancer recurs after radiation therapy, also known as salvage therapy. Cryotherapy is an outpatient procedure.
HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) was approved by the FDA for ablation of the prostate in 2016 but is widely used to treat prostate cancer here in the US. It is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure using ultrasound waves to create heat to a narrow beam by a probe inserted in the rectum. The sound waves are transmitted through the rectal wall to the prostate preserving important structures. It is typically used to treat low risk or intermediate risk prostate cancer. It can be used to treat the whole gland, but it can be used to treat part of the prostate, also known as focal therapy. It has a high chance of maintaining a man's sexual performance, even a man's ejaculation if only focal therapy is done.
Treatment options for cancer once it has spread outside of the prostate include medications to reduce your testosterone, also called ADT (Androgen Deprivation Therapy). These are typically given by a shot in the doctor's office or by removing the testicles.
Immunotherapy, which is a biological therapy that uses your own immune system to fight cancer. It is given 3 times, similar to how vaccines are given and work. However, it is only used when ADT is no longer working.
There are new oral medications that can be given in addition to ADT to either lower Testosterone production or block the effect of Testosterone on the cancer cell. These are new novel therapies that are in pill form and taken daily.
Also, if the cancer has spread to bones, in addition to ADT, Radionucleotides can be infused to target the bone.
Chemotherapy, which are drugs to kill fast growing cells including cancer cells is only used when cancer has spread outside of the prostate.
Supplements or Natural Products for Prostate Cancer
For prostate cancer, like any cancer, there is no natural alternative to conventional medicine. Although, there are natural remedies that can help with your treatment plan and keep your body healthy enough to fight the cancer. Herbal supplements and vitamins haven't been proven to treat cancer or to affect recovery, but there is data that shows an increase in prostate health. The most common are:
Vitamin D
A vitamin D deficiency has been known to be a symptom of prostate cancer. Taking a vitamin D supplement will help overall health as well.
Korean Ginseng
An ancient cherished root, Korean Ginseng has been attributed to good health and longevity. There have been some tests that have shown that men who take Korean Ginseng have experienced better results in prostate health and less risk of prostate cancer.
Echinacea
A special herb attributed to supporting the immune system. As your prostate cancer is treated, your immune system will be compromised. This herb will keep your immunity strong and you healthy.
When to See a Doctor in Atlanta for Prostate Cancer
If your primary care physician finds that you have an Elevated PSA or If you feel that your treatment or medication hasn't been effective in fighting your prostate cancer, contact your doctor or specialist immediately. Battling cancer comes with a great deal of uncertainty and stress. You've probably spent hours searching online for "prostate cancer treatment near me" or "urology clinic for prostate cancer near me."
There are many options for treating prostate cancer depending on how aggressive your prostate cancer is. If you have aggressive prostate cancer treatment is either with surgery and/ or radiation. You may require further treatment if your cancer has spread.
Treatments and Surgery For Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the 2nd leading cause of cancer death in American men. Fortunately, if caught early, it is very treatable with excellent cure rates. There are several types of treatment, but the majority of prostate cancer is treated with surgery. Surgery is done to remove the entire prostate, which is an organ that is responsible for fertility. If your prostate is removed, you will not be able to have children naturally anymore, though outside of fertility, the prostate has no role.
Ablative therapies (killing the prostate without removing it) are also available. Radiation therapy in various forms is the most popular form of ablative therapy and uses radiation to kill the cancer. Cryotherapy or freezing the prostate to kill the cancer is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure but has a high rate of erectile dysfunction. A newer form of ablative therapy is HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) which uses heat to kill the gland. HIFU is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure and has the best chance to maintain sexual function compared to other therapies but its long-term efficacy in the US is not known. HIFU can be used to treat as little or as much of the prostate as needed, this is known as focal therapy. We at Advanced Urology are currently the only group offering this cutting-edge treatment option.
How To Know if the Atlanta Prostate Cancer Treatment Is Right for You
In many cases, your doctor or urologist will recommend surgery before any other treatment. Unless the prostate tumor is small or the patient has a compromised immune system, surgery is a great treatment option with excellent cure rates exceeding 90% for most patients. Removing the tumor or the prostate entirely is the best way to ensure the cancer doesn't spread to other organs or affects other bodily functions.
If you suspect you're suffering from prostate cancer or if you've recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer, you should seriously consider surgery as your first option for treatment. Some other factors to consider regarding any surgery are:
- Age - The older you are the more risks there are to surgery.
- Immune system - If your immune system is easily compromised from a separate condition or disease, you're at more of a risk for infection from surgery.
- Aversion to surgery - If your religion or culture is against surgical procedures, other options are available.
Your doctor or specialist will take all those factors into account before recommending surgery after looking over your tests and screening results.
The Types of Surgery for Prostate Cancer
The surgical treatments for prostate cancer can be life-saving. The surgical treatment can be performed in several different ways:
- Robot assisted surgery - This procedure uses the assistance of a robot to perform the surgery. The robot is inserted into the body through several small incisions while the doctor controls it. This allows for a more precise, less invasive procedure, less blood loss, and quicker recovery time. Click here to learn more about our Advanced Robotic Surgery Program.
- Open surgery - This surgery removes the prostate through an incision on the abdomen.
Many of our urologists at Advanced Urology have fellowship training in either cancer and/or minimally invasive techniques such as robotic surgery and have performed hundreds of cancer surgeries during their career. This allows them to grant their patients excellent cure rates that exceed 90-95% for most patients. The majority of patients who have surgery for prostate cancer with a urologist at Advanced Urology, have their prostate removed robotically, with minimal blood loss, and are sent home the next morning after surgery. They are on pain medications on average for 1 week after surgery. We want our patients to be walking the same day as surgery, and most are having a regular meal the same day as their surgery. Most patients can resume normal activity without restriction about 1 month after surgery. Until then, most patients can return to normal activity with the exception of heavy lifting.